Production Process of PVC Laminated Tarpaulin
The production process of PVC laminated tarpaulin involves multiple steps to ensure durability, weather resistance, and adhesion between layers. Below is a detailed breakdown of the manufacturing process:
1. Raw Material Preparation
Base Fabric: Typically polyester (PET) or nylon woven fabric (e.g., 500D, 1000D) for strength.
PVC Resin: The primary coating material, mixed with additives:
Plasticizers (e.g., DINP, DOP) for flexibility.
Stabilizers (e.g., calcium-zinc) for heat resistance.
UV inhibitors for sunlight protection.
Flame retardants (if required).
Color pigments (for desired appearance).
2. Fabric Pre-Treatment
Heat Setting: The fabric passes through an oven to remove moisture and wrinkles.
Scorching (Optional): Burns off loose fibers for smoother lamination.
Primer Coating (Optional): Enhances PVC adhesion to the fabric.

3. PVC Film Preparation
The PVC resin mix is extruded into a thin, uniform film.
Calendering: The molten PVC is pressed into sheets of precise thickness (e.g., 0.3mm–0.8mm).

4. Lamination Process
Method 1: Hot Melt Lamination (Most Common)
The PVC film is placed over the fabric.
Passed through heated rollers (120–200°C) under high pressure.
The heat melts the PVC, bonding it permanently to the fabric.
Method 2: Adhesive Lamination
A thermosetting adhesive (e.g., PU or acrylic) is applied between the PVC film and fabric.
Cured under heat for a strong chemical bond.
5. Cooling & Solidification
The laminated fabric is cooled rapidly to lock the layers together.
Ensures no warping or delamination.
6. Surface Finishing
Embossing: Rollers add texture (e.g., matte, glossy, or anti-slip patterns).
Top Coating (Optional):
PVDF coating for enhanced UV resistance.
Acrylic coating for better waterproofing.
7. Quality Control Tests
Peeling Strength Test (ASTM D751/ISO 2411) – Ensures layers won’t separate.
Water Resistance Test (ISO 811) – Checks for leaks.
Tensile Strength Test (ISO 13934-1) – Measures fabric durability.
Flame Retardancy Test (EN 13501/NFPA 701) – For safety compliance.
8. Cutting & Sewin
The laminated fabric is cut to size.
Edges are hemmed, welded, or reinforced with webbing/keder strips.
Grommets or eyelets are added for tie-downs.
9. Final Inspection & Packaging
Visual checks for defects (bubbles, uneven coating).
Rolled or folded for shipping.
Key Factors Affecting Quality
Temperature/Pressure Control: Critical for consistent lamination.
PVC Formula: Balances flexibility, UV resistance, and adhesion.
Fabric Quality: High-denier polyester ensures tear resistance.
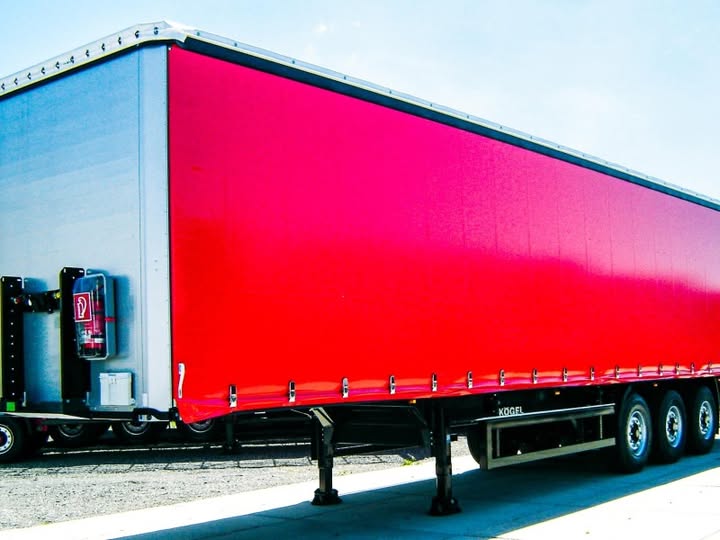
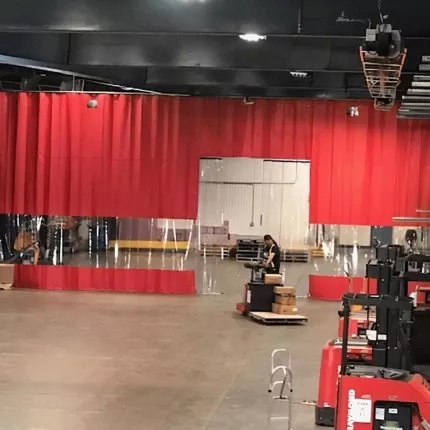
Applications of PVC Laminated Tarpaulin
Heavy-duty truck covers
Industrial curtains
Marine and stadium roofing
Military and disaster relief tents




